
intro_timeseriesdatasets
Source:vignettes/intro_timeseriesdatasets.Rmd
intro_timeseriesdatasets.RmdIntroduction
The timeSeriesDataSets package provides a
collection of time series datasets for R, with suffixes
(_ts, _mts, _tbl_ts) added based
on the object type and class to clearly indicate their time series
nature. This helps users easily identify time series datasets by their
names. The datasets are sourced from various R packages, with modified
names to reflect their time series structure. In this vignette, we will
explore these datasets and demonstrate how to use them in your
analyses.
Getting Started
To use the datasets from the timeSeriesDataSets package,
you first need to install and load the package. You can install it from
CRAN or from a local source if you’re developing it.
# Install the package from CRAN
# install.packages("timeSeriesDataSets")
# Load the package
library(timeSeriesDataSets)Datasets Overview
The AirPassengers_ts dataset is a classic time series
that shows the monthly number of passengers from 1949 to 1960. Note that
the timeSeriesDataSets package adds a _ts suffix to
identify datasets like AirPassengers_ts as time series.
Time Series Visualization
You can use these time series datasets for various time series analyses and visualizations. For example, you can plot the data to visualize trends over time.
# Convert AirPassengers to a data frame for use with ggplot2
air_df <- data.frame(
Month = time(AirPassengers_ts),
Passengers = as.numeric(AirPassengers_ts)
)
# Time series plot
ggplot(air_df, aes(x = Month, y = Passengers)) +
geom_line(color = "blue") +
labs(title = "International Airline Passengers (1949-1960)",
x = "Date", y = "Number of Passengers") +
theme_minimal()
#> Don't know how to automatically pick scale for object of type <ts>. Defaulting
#> to continuous.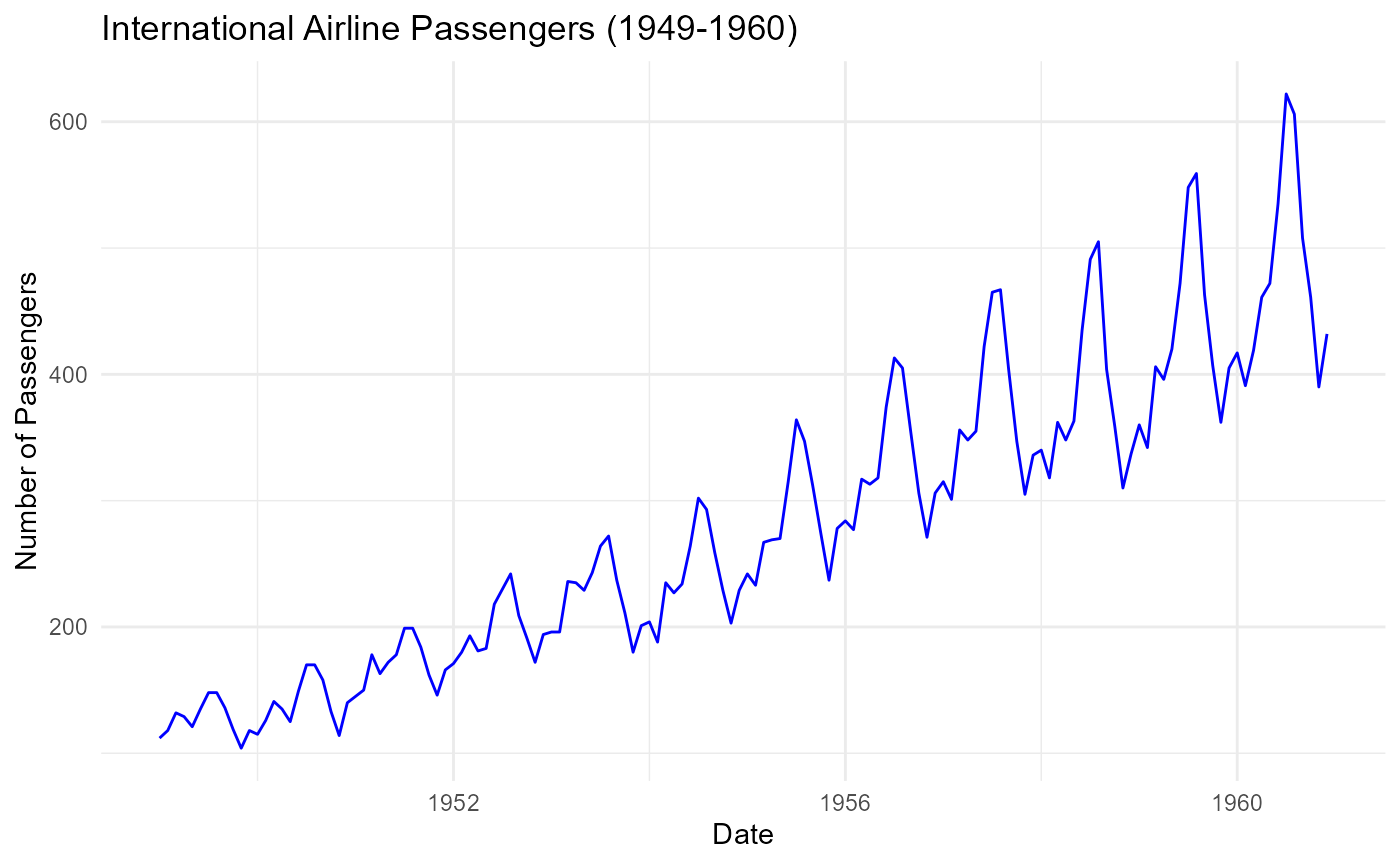
Trend and Seasonality
We can extract the trend and seasonality components from the decomposed time series.
# Decompose the time series
decomposed_ap <- decompose(AirPassengers_ts)
# Extract trend and seasonality
trend <- decomposed_ap$trend
seasonal <- decomposed_ap$seasonal
# Create a data frame for ggplot2
decomposed_df <- data.frame(
Month = time(AirPassengers_ts),
Passengers = as.numeric(AirPassengers_ts),
Trend = trend,
Seasonal = seasonal
)
# Plot trend and seasonality
ggplot(decomposed_df, aes(x = Month)) +
geom_line(aes(y = Passengers), color = "blue", alpha = 0.6) +
geom_line(aes(y = Trend), color = "red", linetype = "dashed") +
geom_line(aes(y = Seasonal + mean(Passengers)), color = "green", linetype = "dotted") +
labs(title = "Trend and Seasonality in AirPassengers Dataset",
x = "Date", y = "Number of Passengers") +
theme_minimal()
#> Don't know how to automatically pick scale for object of type <ts>. Defaulting
#> to continuous.
#> Warning: Removed 12 rows containing missing values or values outside the scale range
#> (`geom_line()`).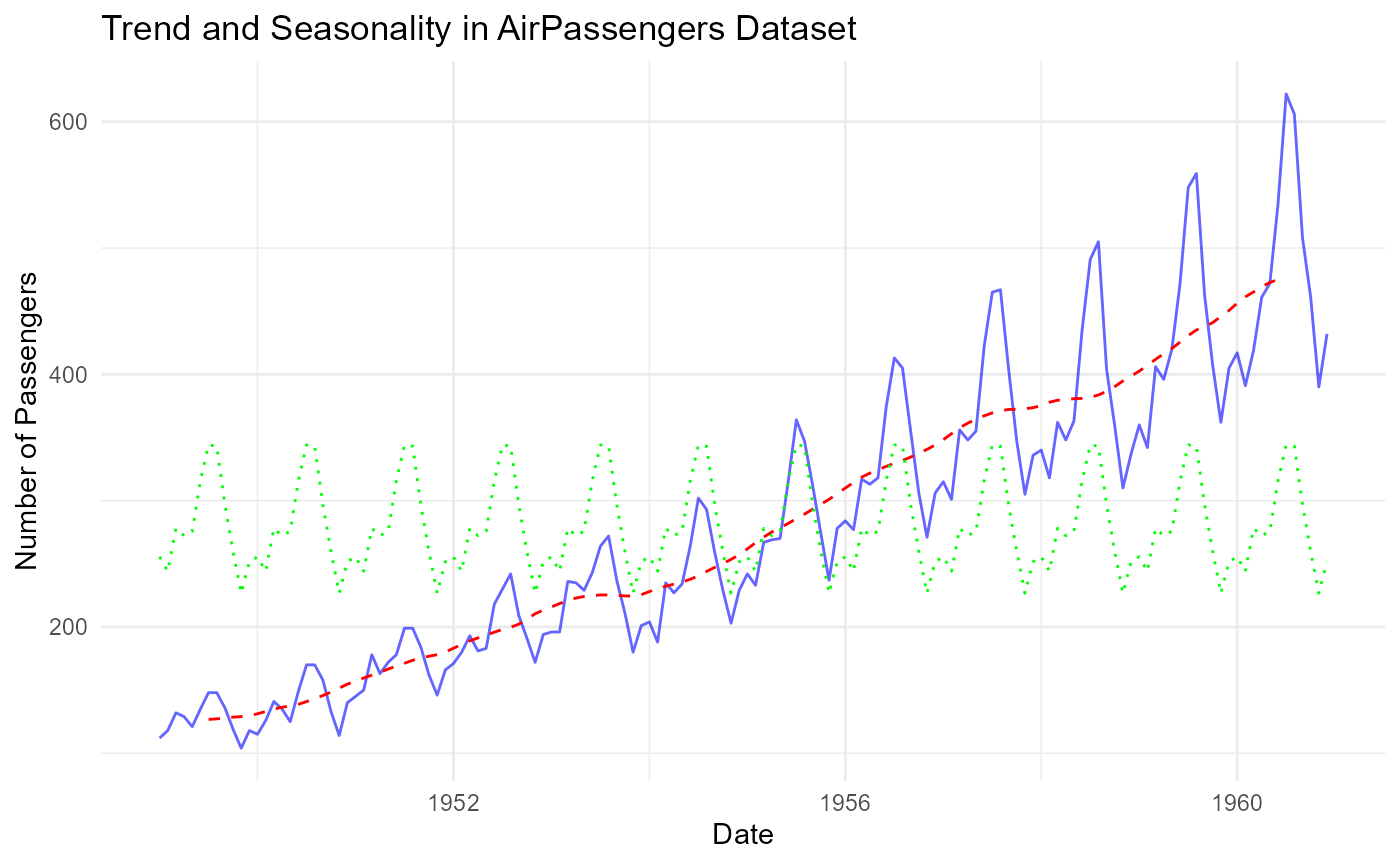
Conclusion
The timeSeriesDataSets package provides a rich
collection of time series datasets for analysis. With these datasets,
you can perform various time series analyses and gain insights into
trends and patterns over time. The timeSeriesDataSets
package aims to provide a comprehensive set of time series datasets that
have been sourced from various R packages and modified to fit specific
time series object conventions. This package should be a valuable
resource for anyone working with time series data in R.
We encourage you to explore the datasets and leverage the functionality of this package to enhance your time series analysis and research.